

Many clients ask for a deep tissue massage because they are stiff and sore, and they have painful knots and kinks in their muscles. Deep tissue massage is very popular among athletes and those involved in strenuous physical activity, whether for business or pleasure, and it does indeed have benefits that reach beyond the typical Swedish massage.
Swedish vs Deep Tissue: What’s The Difference?
Swedish Massage
A typical Swedish massage uses long sweeping strokes for the purposes of relaxation, loosening the fascia, reducing blood pressure, and stimulating the parasympathetic nervous system. Although a Swedish massage can use a variety of techniques including deep tissue, the primary objective is to relax the client and provide both mental and physiological benefits. A Swedish session primarily benefits the muscles that are close to the surface and the fascia, which is the web-like substance that covers the musculature. Although knots and adhesions may be worked on during a Swedish session of massage, they’re not the focus of the session.
It’s not uncommon for the client to experience some stiffness on the day following a Swedish session, particularly if it’s the client’s first massage or if it’s been a long time since the last massage. This is normal and shouldn’t last long. Drinking ample amounts of water can help alleviate any discomfort.
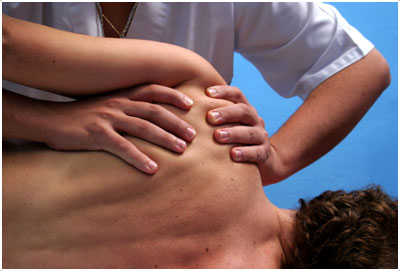
Deep Tissue Massage
A deep tissue massage focuses on the tissues that lie deeper within the body. Although some of the same techniques may be used in deep tissue that are used in Swedish, the focus of the session is different. Deep tissue massage tries to eliminate the adhesions, trigger points, and knots that may be deep within the tissues and difficult to reach. Deep tissue is a frequent component of sports massage and, like sports massage, isn’t intended for relaxation but for therapy. Left untreated, the knots and adhesions in the muscles can deteriorate into more serious medical issues, so deep tissue work or a sports massage can prevent further muscle damage.
Deep Tissue Massage Benefits
The benefits of deep tissue massage far outweigh any momentary discomfort caused by the session. When trigger points are left untreated, they can adversely affect many other parts of the body, depending on the location of the trigger point. For example, a trigger point in the popliteus can result in a restricted function of the hip rotators and the piriformis, resulting in morning stiffness and mobility issues. Trigger points in other areas can be extremely painful and can limit muscle function in the affected tissue as well as those muscles that surround it. They can also cause additional trigger points as the body tries to compensate for the damaged area.
Adhesions can occur in any part of the body, and unresolved adhesions can cause physiological difficulties. A deep tissue massage can alleviate both trigger points and adhesions and restore full function to the affected areas.
Pain And Discomfort Of Deep Tissue Massage
The best way to eliminate the pain and discomfort of deep tissue massage is to have regularly scheduled Swedish sessions. Regular massage sessions keep the muscles in good form and free of knots, trigger points, and adhesions that can build up over time. They also help keep the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system functioning efficiently, so metabolic wastes are eliminated and not allowed to accumulate in the tissues.
Another excellent method for eliminating the pain and discomfort of a deep tissue session is to drink ample quantities of water after the session and for at least two to three days subsequent. Water helps reduce blood pressure, which is good for the heart. It also helps in the elimination of metabolic waste, such as lactic acid, which can cause stiffness in the tissues if it’s not removed.
Those clients who haven’t had a massage in a while and want a deep tissue session may experience some stiffness and soreness following the session. However, a deep tissue session shouldn’t cause pain, there should be no bruising, and any residual discomfort shouldn’t last beyond two to three days.


 Hey Congratulations you’ve found out your having a baby –What Now!
Hey Congratulations you’ve found out your having a baby –What Now!